Service Definition
Drivers should always drive at an appropriate, safe, speed. One way to contribute towards this is to ensure the driver always and everywhere knows the speed limit in force.
Traditionally this has been via fixed speed limit signs and road marking but now the information can also be delivered to drivers digitally, through data services. These services include through VMS, showing variable (dynamic) speed limits, and through in-vehicle devices. To achieve these data services, information on the speed limits in force needs to available and accessible.
The purpose of this chapter is to share relevant information and guidance for road operators on contributing to speed limit information services, covering functional, technical and common look and feel requirements.
Functional Requirements
Functional architecture
The following diagram gives a schematic overview of the typical system architecture required for a speed limit information service, covering
- static speed limit information collection, storage and updating
- dynamic (variable) speed limit (VSL) data processes
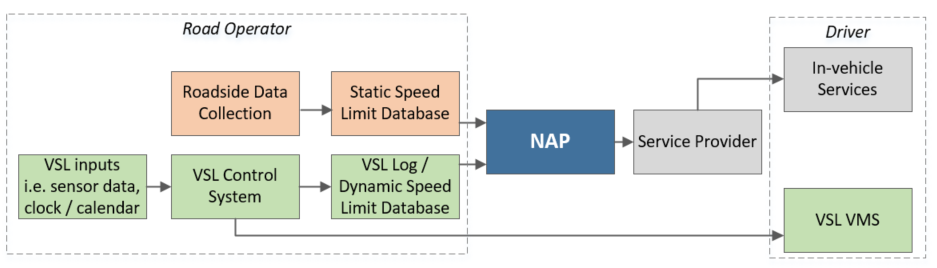
Figure 31: Diagram of a typical system architecture and information flow of a speed limit service - FR1: Source, scope and quality of speed limit information provided by content owners to content providers must both be defined and part of data interface descriptions.
- FR2: Speed limit information collected and information provided by content owners to content providers must be based upon both a consistent geographic reference model and a time validity model, which both must be agreed among parties participating in the service and part of data interface descriptions.
- FR3: If a speed limit information service involves road operators and service providers, information exchange platform systems between road operators and service providers should be implemented to update the databases
- FR4: The frequency of the updates of the speed limit databases should be agreed (and published) and ensured by parties participating in the service.
- FR5: A feedback loop between service providers and the road operators should be put in place to ensure correct data provision and integration in the speed limits databases.
Functional decomposition[1] and interfaces
The function of the service is to provide speed limit information to road users either pre-trip, for more accurate trip planning, or on-trip information. This may be demand responsive or led by the information providers. In Europe, both public and private information providers are involved in this information provision (see organisational requirements). Hence the decomposition of the whole service into sub-functions is necessary identifying interfaces to be standardised.
The following figure shows the typical functional architecture of a “Speed limit information service”. The vertical lines show the identification of interfaces to be optimised:
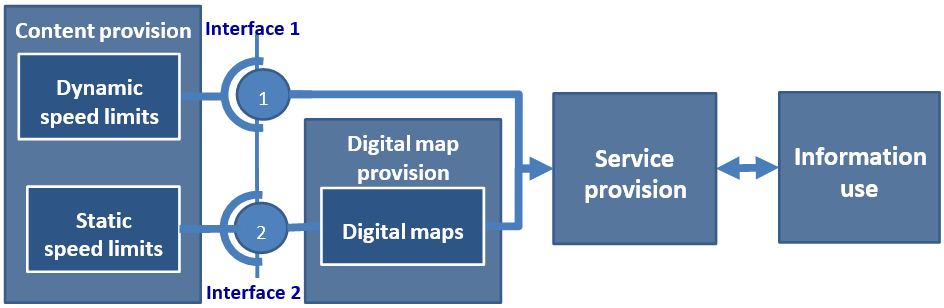
Interface Requirements
Interface requirement interface 1 – Dynamic speed limits (see also Technical requirements):
- FR6: To foster interoperability between all involved parties the sub-functions service and content provision should require/provide an interface with the appropriate information structure for dynamic (variable) speed limits, which is specified in Deployment Guideline TMS-DG02 „variable speed limit“.
Interface requirement interface 2 – Static speed limits (see also Technical requirements):
- FR7: To foster interoperability between all involved parties the sub-functions service provision and digital map provision should require/provide an interface with the appropriate information structure for static speed limits
- Data content:
- starting and ending point
- direction
- speed
- physical exchange format
- location reference
- Data content:
[1] The ITS service is „distributed“ over more than one administration (cross-border, cross-regional) for operation, i.e. different road operators and other parties are involved, providing „logical sub-functions“. Between the distributed functions interoperability must be guaranteed by properly specified interfaces.