Affected ITS-Core Services:

Background
The delivery of ITS Core services to road users has evolved and used a multitude of communication channels (e.g. spoken traffic information in FM radio, Variable Message Signs, Internet portals) since decades. This is the basic idea behind the illustration in Figure 10.
When looking to the content segment, road authorities and operators have traditionally heavily relied on own detectors along their network, complemented by e.g. Floating Phone Data / Floating Car Data and incident reporting by road users. This delivery process including its sourcing is represented in the stylised value chain for traffic information.
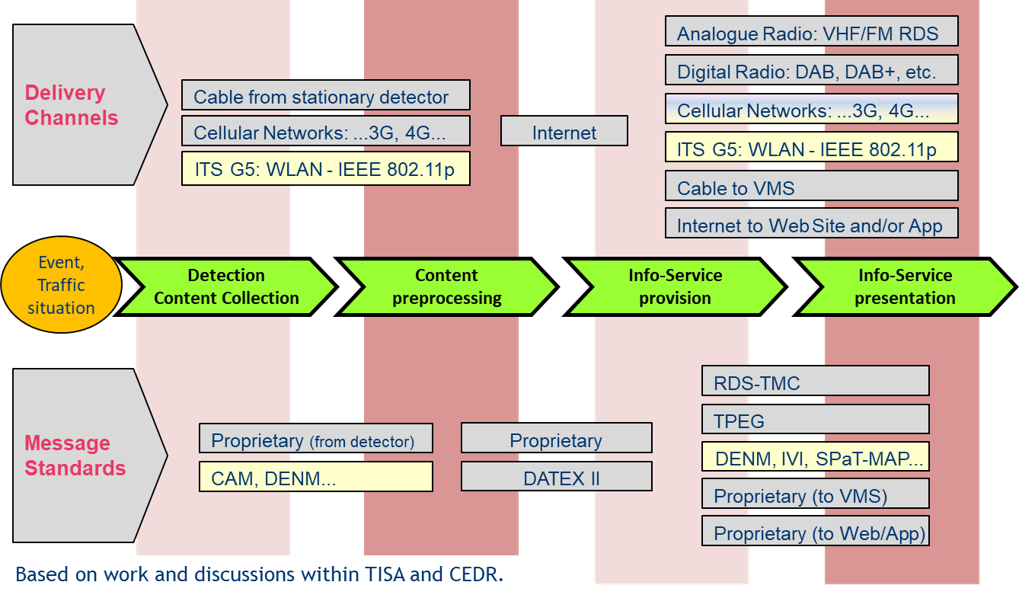
The advent of Cooperative ITS (C-ITS) has opened up another channel to this value chain. For simplification reasons we stick here to the linear value chain and do not argue on C-ITS leading to a circular information flow or even a value web, as discussed elsewhere [Berndt et al. 2018]. C-ITS is defined according to standardisation in CEN/ISO and ETSI as a subset of the overall ITS that communicates and shares information between ITS Stations (ITS-Ss) to give advice or take actions with the objective of improving safety, sustainability, efficiency and comfort beyond the scope of stand-alone ITS. The definition embraces the concept of ITS stations that can be located either in vehicles, at the roadside, in the traffic control centre or related to personal mobile devices. The Delegated Regulation on C-ITS – which has been adopted by European Commission on 13.03.2019 but has not come into force – has emphasised the peer-to-peer network character as well as the security and trust implications of a „broadcast system“. It has defined C-ITS as intelligent transport systems that enable ITS users to cooperate by exchanging secured and trusted messages using the EU C-ITS security credential management system.
As it is illustrated in Figure 10 C-ITS represents another content source and also another communication channel into the vehicles. As stated in the European C-ITS strategy (COM (2016) 766), a C-ITS message can be communicated in the vicinity by ITS G5 (short range communication) or by existing cellular networks (long range communication). These communication technologies have been tested by road authorities and operators for several years (Field Operational Tests, Pilots and Deployment Initiatives) and can be considered mature for provision of initial C-ITS services. Developments in progress that are not (yet) represented in Figure 10 comprise the following streams:
- Alternative technologies for short range communication are meanwhile specified (LTE V2X as part of 3GPPP Release 14) and increasingly tested under different conditions (e.g. lab, test track). The commercial availability of LTE V2X equipment however remains a challenge, at least for the European market (JRC 2019). Specifications will evolve towards 5G V2X and 5G-NR as part of 3GPPP Release 16 in 2020.
- Data from vehicles can serve as a valuable source of Safety Related Traffic Information (SRTI). A Proof-of-Concept of the Data Task Force of the High-Level Meeting on Connected and Automated Driving involves Member States, OEMs and service providers. The One-Year-Proof-of-Concept has been launched in June 2019. It aims at assessing the road safety contribution of sharing road safety related data in public and private cooperation. Despite of its valuable contribution, this sourcing channel does not involve C-ITS in the definition boundaries of the Delegated Regulation.
The initial deployment of mature C-ITS services is organised via Member State driven C-ITS pilots that collaborate in the C-Roads Platform. This flagship, comprising of currently 18 European states, collaborates on harmonised specifications and communication profiles. The latest Release 1.5 of C-Roads harmonised C-ITS specifications (published in August 2019) contains a bundle of documents:
- C-ITS Infrastructure Functions and Specifications,
- Common C-ITS Service Definitions,
- Roadside ITS G5 System Profile,
- Mobile Roadside ITS-G5 System Profile,
Specification for interoperability of backend hybrid C-ITS communication.